Abstract
Background: Novel treatment approaches including chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T therapy and bispecific antibodies (Abs) have shown remarkable efficacy in highly pretreated multiple myeloma (MM) patients. With recent approval of BCMA-targeted CAR T in MM, and other agents in development, CAR T is poised to become more widely used in relapsed/refractory disease (RRMM). However, the prognosis, clinical outcome, and treatment approach to RRMM patients presenting with relapsed disease after CAR T are unknown.
Methods: Demographics, disease characteristics and post-study outcomes were collected retrospectively in patients who relapsed after BCMA-targeted CAR T therapy at a single academic institution (Mount Sinai Hospital, NY). We identified 74 patients who previously enrolled on 1 of 6 clinical trials. At the data cutoff (July 2021), 4 patients died on trial and were not evaluable, whereas 31 patients had left the trial due to disease progression (PD) and were included. Five patients had received CAR T reinfusion after initial PD, in which case date of PD after reinfusion was considered the start of post-CAR T evaluation. This retrospective study was approved by the institutional review board (GCO#:11-1433). Survival analyses and follow-up duration were calculated by (reverse) Kaplan-Meier analysis.
Results: At time of PD after CAR T, the 31 patients had a median age of 61 years (range 35-75) and 19 (61%) were male. Median time from diagnosis was 74 months (range 22-282). Of these 26 patients (84%) had high-risk cytogenetics on FISH [t(4;14), t(14;16), t(14;20), loss of TP53 or 1q21 gain]. Patients were highly pretreated with a median of 5 prior lines (range 1-18). 28 patients (90%) had received prior autologous stem cell transplant. Patients were refractory to various treatments: thalidomide (6% refractory), lenalidomide (74%), pomalidomide (84%), bortezomib (61%), carfilzomib (87%), ixazomib (23%), CD38-mAb (97%), alkylating agents (54%), venetoclax (19%) and selinexor (19%). Most (84%) were triple-class refractory. Fifteen patients (48%) had received DCEP and 4 (13%) had received prior treatment with non-BCMA-targeted bispecific Ab.
Upon CAR T relapse, 12 patients (39%) progressed with new/increased extramedullary disease. Information on additional MM treatment was available for 28 patients (90%); 1 patient was treated with cytarabine for MDS, 1 received no treatment, and 1 was lost to follow-up. Median time from relapse to first subsequent treatment was 30 days (range 0-201). Patients received a median of 2 additional treatment lines (range 0-8). The most common initial treatment after CAR T relapse was chemotherapy with (V)DCEP or VD-PACE (10/28, 36%). Stem cell boost with prior chemotherapy was part of the initial approach in 5 patients (18%) and was performed in 12 patients at any time after CAR T relapse (43%). Five patients (18%) were treated with bispecific Ab immediately after CAR T and 12 (43%) received bispecific Ab therapy at any point after CAR T. Selinexor-based regimens were used in 3 (11%) patients immediately after and in 10 (36%) at any point after CAR T relapse. Best response to initial treatment varied widely with 46% ORR (7 CR, 5 VGPR, 1 PR, 7 SD, 8). Median time to progression was 105 days (95% CI: 78-204) for the initial treatment after CAR T.
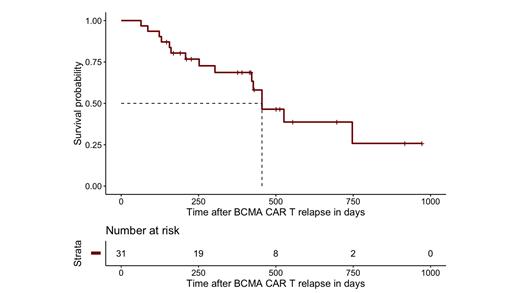
Across various treatment lines after relapse, 33 occurrences of durable response (>120 days, range 128-555) were noted, of which 8 involving stem cell transplant, 8 involving bispecific Abs (alone or in combination with approved anti-MM agents), 5 involving selinexor-based treatments, 3 with venetoclax and 3 involving a MEK inhibitor. Median PFS of patients transitioning to bispecific Ab therapy immediately after CAR T was not yet reached. At time of analysis, 16 patients (52%) were alive and median overall survival after relapse on CAR T was 15.0 months (455 days, 95% CI: 422-NE) with a median follow-up of 501 days.
Conclusion: RRMM patients relapsing after T cell engager therapy are a challenging population. Studying the prognosis of these patients including response to subsequent therapy will provide important clinical insights, especially as CAR T moves to an earlier treatment setting. Even though, due to selection, our cohort might be biased towards subjects with early CAR T failure, we show that novel agents, including bispecific Abs can cause durable responses in post-CAR T relapse. Updated results will be presented at the meeting.
Richard: Karyopharm, Janssen: Honoraria. Richter: Oncopeptides: Consultancy; X4 Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Sanofi: Consultancy; Antengene: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy; Secura Bio: Consultancy; Astra Zeneca: Consultancy. Chari: Oncopeptides: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Antengene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GlaxoSmithKline: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi Genzyme: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS/Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Secura Bio: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; Millenium/Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; Shattuck Labs: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Seattle Genetics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen Oncology: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Jagannath: Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Karyopharm Therapeutics: Consultancy; Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Legend Biotech: Consultancy; Sanofi: Consultancy. Parekh: Foundation Medicine Inc: Consultancy; Amgen: Research Funding; PFIZER: Research Funding; CELGENE: Research Funding; Karyopharm Inv: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal